SOUND
- Sound is a form of energy and like all other energies, sound is not visible to us.
- It produces a sensation of hearing when it reaches our ears.
- Sound can not travel through vacuum.
- sound waves are longitudinal waves.
Sound travels as successive compressions and rarefactions in the medium. In sound propagation, it is the energy of the sound that travels and not the particles of the medium.
WAVELENGTH
The distance between two consecutive compressions or two consecutive rarefaction is called the wavelength.

The distance between two consecutive compressions or two consecutive rarefaction is called the wavelength.

To and fro motion of an object is known as vibration. This motion is also called oscillatory motion.
Two important properties of any sound:
- Amplitude
- frequency

AMPLITUDE
vibrate.
The amplitude is expressed in metre(m).
The amplitude is expressed in metre(m).
The number of complete oscillations per unit time is called the frequency.
F =(1/T)
The frequency is expressed in hertz (Hz).
- Larger the amplitude of vibration, louder is the sound.
- Higher the frequency of vibration, the higher is the pitch, and shriller is the sound.
All harmonics are overtone but all overtones are not harmonics.
The speed of sound in a medium depends:
In any medium as we increase the temperature the speed of sound increases.
- temperature of the medium.
- pressure of the medium.
In any medium as we increase the temperature the speed of sound increases.
The velocity of sound through a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the density of the gas.
- It is a reflection of sound that arrives at the listener with a delay after the direct sound.
- The sensation of sound persists in our brain for about 0.1 second.
- To hear a distinct echo, the time interval between the original sound and the reflected one must be at least 0.1 second.
- For hearing distinct echoes, the minimum distance of the obstacle from the source of sound must be 17.2 m. This distance will change with the temperature of air. Echoes may be heard more than once due to successive or multiple reflections.
REVERBERATION
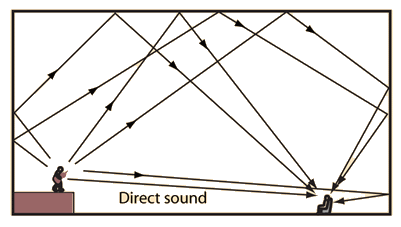
The phenomenon of prolongation of sound due to successive reflections of sound from surrounding objects is called reverberation.
Example:
In stethoscopes the sound of the patient’s heartbeat reaches the doctor’s ears by multiple reflection of sound.
AUDIBLE RANGE
The audible range of sound for human beings extends from about 20 Hz to 20000 Hz (one Hz = one cycle/s). Children under the age of five and some animals, such as dogs can hear up to 25 kHz (1 kHz = 1000 Hz).
INFRASONIC SOUND
Sounds of frequencies below 20 Hz are called infrasonic sound or infrasound.
Example:
Rhinoceroses communicate using infrasound of frequency as low as 5 Hz. Whales and
Example:
Rhinoceroses communicate using infrasound of frequency as low as 5 Hz. Whales and
elephants produce sound in the infrasound range. It is observed that some animals get disturbed before earthquakes. Earthquakes produce low-frequency infrasound before
the main shock waves begin which possibly alert the animals.
Frequencies higher than 20 kHz are called ultrasonic sound or ultrasound.
Example:
Ultrasound is produced by dolphins, bats and porpoises.
Applications:
Example:
Ultrasound is produced by dolphins, bats and porpoises.
Applications:
- Ultrasounds can be used to detect cracks and flaws in metal blocks.
- Metallic components are generally used in construction of big structures like buildings, bridges, machines and also scientific equipment.
- The cracks or holes inside the metal blocks, which are invisible from outside reduces the strength of the structure. Ultrasonic waves are allowed to pass through the metal block and detectors are used to detect the transmitted waves. If there is even a small defect, the ultrasound gets reflected back indicating the presence of the flaw or defect.
- Ultrasonic waves are made to reflect from various parts of the heart and form the image of the heart. This technique is called ‘echocardiography’.
- Ultrasound scanner is an instrument which uses ultrasonic waves for getting images of internal organs of the human body. A doctor may image the patient’s organs such as the liver, gall bladder, uterus, kidney, etc. It helps the doctor to detect abnormalities, such as stones in the gall bladder and kidney or tumours in different organs. In this technique the ultrasonic waves travel through the tissues of the body and get reflected from a region where there is a change of tissue density. These waves are then converted into electrical signals that are used to generate images of the organ. These images are then displayed on a monitor or printed on a film. This technique is called ‘ultrasonography’.
The acronym SONAR stands for Sound Navigation And Ranging.
Let the time interval between transmission and reception of ultrasound signal be t and the speed of sound through seawater be v. The total distance, 2d travelled by the ultrasound is then,
SUPERSONIC SOUND
- Sonar is a device that uses ultrasonic waves to measure the distance, direction and speed of underwater objects.
- Sonar consists of a transmitter and a detector and is installed in a boat or a ship. The transmitter produces and transmits ultrasonic waves. These waves travel through water and after striking the object on the seabed, get reflected back and are sensed by the detector. The detector converts the ultrasonic waves into electrical signals which are appropriately interpreted.
- The distance of the object that reflected the sound wave can be calculated by knowing the speed of sound in water and the time interval between transmission and reception of the ultrasound.
Let the time interval between transmission and reception of ultrasound signal be t and the speed of sound through seawater be v. The total distance, 2d travelled by the ultrasound is then,
2d = v × t
The above method is called echoranging. The sonar technique is used to determine the depth of the sea and to locate underwater hills, valleys, submarine, icebergs, sunken ship etc.SUPERSONIC SOUND
Again if the speed of any substance, specially of an air-craft, be more than the speed of sound in air, then the speed of the substance is called supersonic speed.
ALL THE BEST !!








No comments:
Post a Comment